Discover the full potential of this set of tools designed to enhance GIS data integration and editing within AutoCAD.
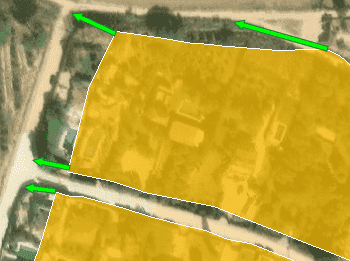
Rubber sheet
Geographically align two or more graphic datasets by defining control points that match known coordinates between them. This process adjusts the geometry of one dataset to fit another, correcting positional inaccuracies and improving spatial consistency across different data sources. It is especially useful when integrating legacy drawings, scanned maps, or misaligned layers into a unified coordinate framework.
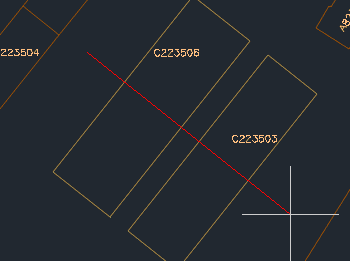
Break
Splits geometries that intersect a specified line, effectively breaking them at the points of intersection. This tool is useful for editing or preparing data for downstream processes that require segmented features, such as network analysis or land subdivision.
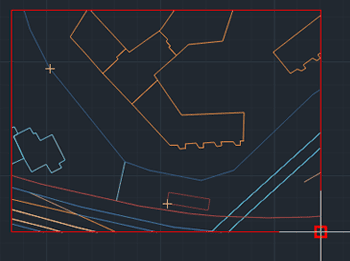
Trim
Enables the use of a closed boundary as a trimming edge to cut intersecting geometries. Users can choose whether to retain the elements inside or outside the boundary, making it a powerful tool for refining drawings, isolating areas of interest, or cleaning up spatial data.
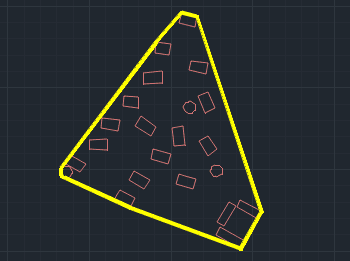
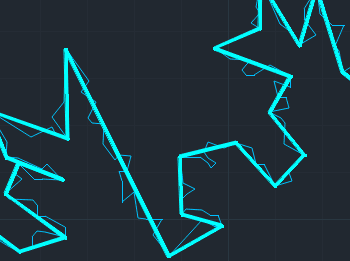
Convex Hull
Generates the smallest convex polygon that completely encloses a selected set of geometries. This operation is useful for creating bounding areas, simplifying complex datasets, and performing spatial analysis. The resulting shape forms the minimal convex envelope around the input features, ensuring optimal coverage with minimal boundary length.
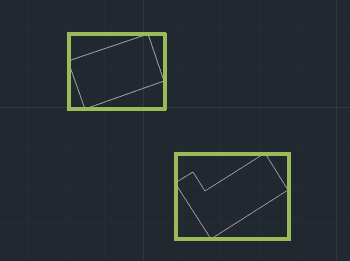
Envelope
Creates an envelope or bounding box for selected geometries. This refers to the smallest rectangular area that fully contains each object. It is commonly used to generalize shapes, define extents, or prepare spatial data for indexing, visualization, or spatial queries. The result is a simplified and standardized representation of the original geometry's outer limits.
Simplify
Reduces the number of vertices (nodes) to simplify polylines or polygons, optimizing geometry complexity while maintaining overall shape integrity. This function is useful for improving performance and visualization of spatial data by decreasing detail where appropriate. When working with adjacent polygons, caution is advised as simplification may create unintended intersections or holes. The tolerance parameter controls the maximum allowed deviation between the simplified geometry and the original.
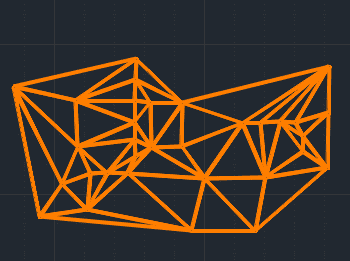
Triangulation
The Triangulation from Points tool generates a mesh of interconnected triangles by connecting a given set of points. This process creates a network of triangles that can be used for surface modeling, terrain analysis, and interpolation of spatial data. The resulting triangular mesh provides a foundation for advanced GIS and CAD operations, ensuring accurate representation of complex spatial structures.
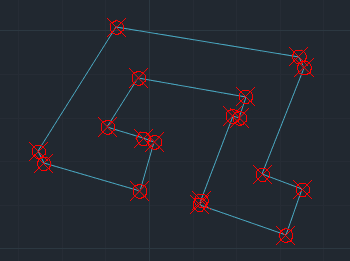
Vertex
The Vertex Extraction tool generates individual point features from the vertices of existing geometries. This function is useful for analyzing, editing, or exporting key coordinate points that define lines, polylines, or polygons.